Are you curious about the consequences of not following the rules in a 1031 exchange? Well, buckle up and get ready to explore the world of penalties in this intriguing real estate practice.
You might be wondering, what exactly is a 1031 exchange? Let’s break it down for you. It’s a tax-deferred exchange that allows real estate investors to swap properties without incurring immediate taxes. Sounds pretty neat, right? But, like any game, there are rules – and penalties for breaking them.
So, if you’re itching to know what happens when you don’t comply with the requirements of a 1031 exchange, stick around because we’re about to dive into the depths of non-compliance penalties. Trust us, you don’t want to miss this!
Contents
- Are There Any Penalties for Non-Compliance in a 1031 Exchange?
- Common Non-Compliance Penalties in a 1031 Exchange
- Additional Considerations for Compliance in a 1031 Exchange
- Key Takeaways: Are There Any Penalties for Non-Compliance in a 1031 Exchange?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What penalties can I face if I don’t comply with the rules of a 1031 exchange?
- 2. Can I face penalties if I miss the 45-day identification period or the 180-day exchange period?
- 3. What are the potential consequences if I use 1031 exchange funds for personal use?
- 4. Can I face penalties for non-compliance even if it was unintentional?
- 5. How can I ensure compliance and avoid penalties in a 1031 exchange?
- Summary
- Conclusion
Are There Any Penalties for Non-Compliance in a 1031 Exchange?
Introduction:
A 1031 exchange is a powerful tool for real estate investors, allowing them to defer capital gains taxes when they sell one property and reinvest the proceeds into another like-kind property. However, with this tax benefit comes the requirement to comply with certain rules and regulations. Non-compliance can result in penalties and potentially negate the tax advantages of a 1031 exchange. In this article, we will explore the penalties associated with non-compliance in a 1031 exchange and provide valuable information to help investors stay on the right side of the law.
Common Non-Compliance Penalties in a 1031 Exchange
When it comes to 1031 exchanges, non-compliance can result in various penalties. It is crucial for investors to be aware of these potential penalties to avoid any negative consequences. Below are some common penalties associated with non-compliance in a 1031 exchange:
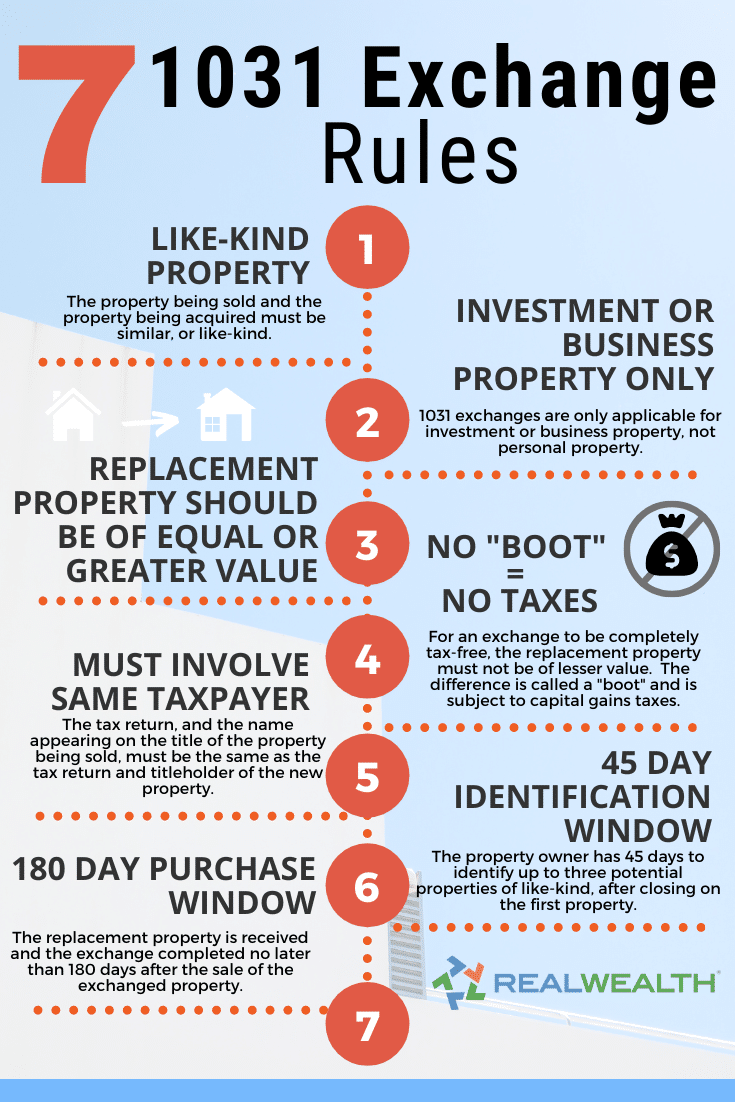
1. Failure to Identify Replacement Properties within 45 Days
The identification period is a critical aspect of a 1031 exchange. Within 45 days of selling the relinquished property, the investor must identify potential replacement properties. Failure to meet this deadline can result in the disqualification of the exchange and the imposition of capital gains taxes. Additionally, if the investor fails to identify the replacement properties correctly or provides an incomplete or invalid identification, it can lead to further penalties or scrutiny from the IRS.
2. Failure to Acquire Replacement Property within 180 Days
Alongside the requirement to identify potential replacement properties, investors must also acquire the replacement property within 180 days of selling the relinquished property. If an investor fails to meet this deadline, it can result in the disqualification of the exchange and potential tax liabilities. It is essential for investors to diligently adhere to this timeframe and ensure the successful acquisition of the replacement property within the designated period.
3. Commingling of Funds
In a 1031 exchange, it is crucial that the funds from the sale of the relinquished property do not come into direct contact with the investor’s personal accounts. Commingling of funds refers to the mixing of sales proceeds with personal funds. This can lead to a disqualification of the exchange and potential tax liabilities. Investors must establish a qualified intermediary (QI) to handle the funds involved in the exchange to ensure compliance and avoid penalties.
4. Use of Proceeds for Personal Benefit
The 1031 exchange rules stipulate that the proceeds from the sale of the relinquished property must be used solely for the acquisition of a replacement property. If an investor uses the proceeds for personal expenses or benefits, it can result in significant penalties, including tax liabilities. It is essential for investors to exercise caution and ensure that the funds are utilized exclusively for the purpose of the exchange.
5. Non-Like-Kind Exchange
Under a 1031 exchange, the replacement property must be of like-kind to the relinquished property. If an investor chooses to acquire a property that does not meet the like-kind requirement, it can result in the disqualification of the exchange and potential tax liabilities. It is crucial for investors to understand the parameters of a like-kind exchange and ensure that they are acquiring properties that meet the necessary criteria.
6. Failure to Meet Holding Period Requirements
Certain types of property in a 1031 exchange are subject to holding period requirements. For example, if an investor chooses to exchange a property that qualifies for capital gains tax rates with a replacement property that is not eligible for such rates, it can result in penalties. Investors must be familiar with the specific holding period requirements and ensure compliance to avoid any adverse consequences.
7. Fraud or Misrepresentation
Engaging in fraudulent activities or misrepresenting information in a 1031 exchange can have severe legal and financial repercussions. The IRS closely monitors these transactions, and any indication of fraud or misrepresentation can trigger audits, penalties, and potential criminal charges. It is crucial for investors to maintain transparency, honesty, and accuracy throughout the entire 1031 exchange process.
Additional Considerations for Compliance in a 1031 Exchange
While understanding the potential penalties for non-compliance is essential, it is equally important to be proactive in ensuring compliance in a 1031 exchange. Here are some additional considerations to help investors stay on the right side of the law:
1. Work with Professionals
Navigating the complexities of a 1031 exchange can be challenging. It is highly recommended to work with experienced professionals, including qualified intermediaries, real estate attorneys, and tax advisors. These professionals can provide expert guidance, ensure compliance, and minimize the risk of penalties.
2. Familiarize Yourself with the Rules and Regulations
Before entering into a 1031 exchange, investors should familiarize themselves with the rules and regulations governing these transactions. Understanding the requirements, timeframes, and restrictions will help investors make informed decisions and avoid unintended non-compliance.
3. Keep Detailed Records
Maintaining thorough and accurate records is crucial for compliance in a 1031 exchange. Recording all transactions, correspondence, and documentation related to the exchange will help provide evidence of compliance if ever required. It is advisable to retain these records for at least the statutory period to ensure full compliance and mitigate any potential issues.
In conclusion, non-compliance in a 1031 exchange can result in various penalties, including disqualification of the exchange, tax liabilities, and possible legal consequences. It is crucial for real estate investors to understand the rules and regulations associated with 1031 exchanges and take proactive measures to ensure compliance. By working with professionals, staying informed, and keeping accurate records, investors can navigate the 1031 exchange process successfully and reap the tax benefits it offers.
Key Takeaways: Are There Any Penalties for Non-Compliance in a 1031 Exchange?
- 1. Non-compliance with 1031 exchange rules can result in significant penalties.
- 2. Penalties may include disqualification of the exchange and the immediate recognition of capital gains.
- 3. Other penalties may include additional taxes and fines imposed by the IRS.
- 4. It is important to consult with a qualified tax professional or exchange facilitator to ensure compliance.
- 5. Proper documentation and adherence to the strict timeline are crucial to avoid penalties in a 1031 exchange.
Frequently Asked Questions
When it comes to a 1031 exchange, it’s crucial to understand the importance of compliance. Failure to comply with the rules and regulations can result in penalties. Here are some common questions regarding penalties for non-compliance.
1. What penalties can I face if I don’t comply with the rules of a 1031 exchange?
Non-compliance with the rules of a 1031 exchange can result in significant penalties. The most common penalty is the disqualification of the exchange, which means you’ll be responsible for paying capital gains taxes on the sale of your property. Additionally, any boot received (non-like-kind property) may also be subject to taxes. It’s essential to work with a qualified intermediary and follow the guidelines to avoid these penalties.
In some cases, the IRS may also impose monetary penalties for non-compliance. These penalties can vary depending on the severity of the violation and can range from monetary fines to criminal charges, in extreme cases. It’s crucial to stay informed about the rules and regulations to ensure a successful and compliant 1031 exchange.
2. Can I face penalties if I miss the 45-day identification period or the 180-day exchange period?
Yes, missing the deadlines associated with a 1031 exchange can lead to penalties. The 45-day identification period is a strict deadline that requires you to identify potential replacement properties within 45 days of selling your relinquished property. Failing to meet this deadline can result in the disqualification of the exchange and the payment of capital gains taxes.
The 180-day exchange period is equally important. You must complete the acquisition of your replacement property within this timeframe. Failing to do so may result in the disqualification of the exchange and potential tax consequences. It’s crucial to be diligent and adhere to these deadlines to avoid penalties and ensure a successful exchange.
3. What are the potential consequences if I use 1031 exchange funds for personal use?
Using 1031 exchange funds for personal use can have severe consequences. If you use the exchange funds for personal expenses or non-like-kind property, you will likely face taxation on the amount used. The IRS considers this as receiving boot, which is the non-like-kind property received in the exchange.
When boot is involved, you may be required to pay taxes on the fair market value of the boot received. Additionally, using exchange funds for personal use can potentially disqualify the entire 1031 exchange, leading to capital gains taxes on the sale of the relinquished property. It’s crucial to use the exchange funds exclusively for acquiring like-kind replacement property to avoid these penalties.
4. Can I face penalties for non-compliance even if it was unintentional?
Yes, unintentional non-compliance can still result in penalties. The IRS expects strict adherence to the rules and regulations surrounding 1031 exchanges, regardless of intent. If you unintentionally violate the guidelines, such as missing a deadline or using exchange funds improperly, you may still face the disqualification of the exchange and potential tax consequences.
To minimize the risk of unintentional non-compliance, it’s crucial to work with a qualified intermediary or a professional who understands the intricacies of 1031 exchanges. These experts can help guide you through the process, ensuring compliance and helping you avoid penalties.
5. How can I ensure compliance and avoid penalties in a 1031 exchange?
To ensure compliance and avoid penalties in a 1031 exchange, it’s essential to stay informed and work with professionals who specialize in these transactions. Here are some steps you can take:
First, consult with a qualified intermediary who can guide you through the process and ensure compliance with the rules and regulations. They will help you meet the deadlines, properly identify replacement properties, and handle the exchange funds to prevent unintentional violations.
Additionally, familiarize yourself with the IRS rules and regulations concerning 1031 exchanges. Understanding the requirements will help you make informed decisions and avoid common pitfalls. Lastly, maintain detailed documentation of the exchange process to demonstrate compliance if ever requested by the IRS. By following these steps, you can increase the likelihood of a successful 1031 exchange without any penalties for non-compliance.
Summary
If you don’t follow the rules of a 1031 exchange, you could face penalties. These penalties can include paying taxes on the gain you deferred, as well as additional fines and interest. It’s important to understand the requirements and stay compliant to avoid these consequences.
Conclusion
In a 1031 exchange, it’s crucial to play by the rules or else you may be penalized. This can mean paying taxes you deferred and facing additional fines and interest. Stay informed and follow the guidelines to ensure a successful exchange.

buy ventolin online europe: Ventolin inhaler – ventolin in usa
ventolin inhaler non prescription
rybelsus price: rybelsus – rybelsus
generic lasix: cheap lasix – lasix 40mg
canada pharmacy 24h: Online medication home delivery – canadian pharmacy 365
indianpharmacy com: Indian pharmacy online – best india pharmacy
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.