The topic we’re exploring today is “How Does a 1031 Exchange Affect Depreciation?” If you’re unfamiliar with these terms, don’t worry—I’m here to break it down for you in a simple and easy-to-understand way. So, let’s dive in and unravel the ins and outs of this fascinating topic!
Picture this: you’re in the world of real estate, buying and selling properties like a pro. You’ve probably heard of something called a 1031 exchange, but what exactly does it have to do with depreciation? Well, my friend, that’s what we’re here to find out. Strap on your virtual hard hat, because we’re about to explore the relationship between these two concepts.
Now, you may wonder, “What is depreciation?” Simply put, it’s the decrease in value that occurs over time for an asset—like a property. Depreciation can have a significant impact on your taxes and financial strategies. And here’s where the 1031 exchange comes into play. It’s a powerful tool that allows you to defer taxes when you exchange one investment property for another. But how does this impact the depreciation of the property? Buckle up, because I’m about to spill the beans on this intriguing connection!
Contents
- How Does a 1031 Exchange Affect Depreciation?
- Benefits of a 1031 Exchange
- Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of a 1031 Exchange
- Key Takeaways: How Does a 1031 Exchange Affect Depreciation?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- 1. What is a 1031 exchange and how does it work?
- 2. Does a 1031 exchange affect the depreciation recapture tax?
- 3. Can I continue depreciating the replacement property after a 1031 exchange?
- 4. Can I do a partial 1031 exchange and still benefit from depreciation?
- 5. Are there any restrictions on depreciation deductions after a 1031 exchange?
- Explained: What Role Does Depreciation Play In A 1031 Exchange? (Michael Brady & Alex Shandrovsky)
- Summary
How Does a 1031 Exchange Affect Depreciation?
A 1031 exchange, also known as a like-kind exchange, is a tax-deferred transaction that allows real estate investors to defer capital gains tax when selling a property and reinvesting the proceeds in the purchase of another property. While a 1031 exchange offers many tax advantages, it also has implications for depreciation. In this article, we will explore how a 1031 exchange affects depreciation and the potential benefits and considerations for real estate investors.
Understanding Depreciation in Real Estate
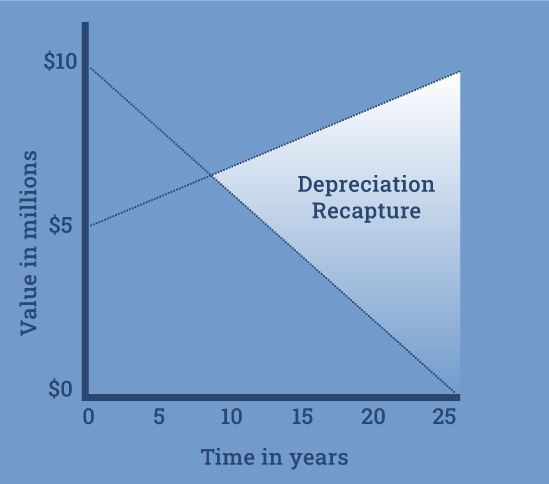
Depreciation is a tax deduction that allows real estate investors to recover the cost of an income-producing property over its useful life. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) allows investors to spread out the property’s cost over a predetermined period of time, typically 27.5 years for residential rental properties and 39 years for commercial properties. Each year, investors can deduct a portion of the property’s value as a depreciation expense on their tax returns, which reduces their taxable income and overall tax liability.
Depreciation is a valuable tax benefit for real estate investors as it allows them to offset rental income and other gains associated with their investment properties. However, when a property is sold, any accumulated depreciation must be recaptured and taxed at a higher rate known as the depreciation recapture tax. This can significantly reduce the investor’s tax benefits and overall return on investment. This is where a 1031 exchange comes into play.
How a 1031 Exchange Impacts Depreciation
One of the main benefits of a 1031 exchange is the ability to defer taxes on the capital gains from the sale of a property. By reinvesting the proceeds from the sale into a like-kind property, investors can defer paying taxes until they sell the replacement property without being subject to depreciation recapture tax. This means that the accumulated depreciation on the relinquished property carries over to the replacement property, allowing investors to continue to depreciate the new property over its useful life.
For example, if an investor sells a rental property that has been depreciated for 10 years and purchases a new rental property in a 1031 exchange, they can continue to depreciate the new property for the remaining years of its useful life. The deferred taxes from the sale of the relinquished property are not due until the replacement property is sold without utilizing another 1031 exchange.
It’s important to note that while a 1031 exchange allows for the deferral of taxes, it doesn’t eliminate them completely. When the replacement property is eventually sold, the accumulated depreciation and any additional gains will be subject to taxation. However, many investors find that they can strategically utilize 1031 exchanges to continue deferring taxes and potentially maximize their overall return on investment.
Benefits of a 1031 Exchange
1. Tax Deferral
A 1031 exchange allows investors to defer capital gains tax on the sale of a property, which can help them preserve their cash flow and reinvest the proceeds in a new property.
2. Increased Buying Power
By deferring taxes, investors have more funds available to invest in a replacement property, potentially allowing them to acquire a higher-value property or multiple properties.
3. Portfolio Diversification
A 1031 exchange provides investors with the opportunity to diversify their real estate holdings by exchanging into different types of properties in different locations.
Tips for Maximizing the Benefits of a 1031 Exchange
1. Plan Ahead
To fully take advantage of the tax benefits of a 1031 exchange, it’s important to plan ahead and identify potential replacement properties before selling the relinquished property.
2. Consult with Professionals
Working with a qualified intermediary and tax advisor who specialize in 1031 exchanges can help ensure the transaction complies with IRS regulations and maximize the tax benefits.
3. Consider Fractional Ownership
Sometimes referred to as Tenancy in Common (TIC) investments, fractional ownership allows multiple investors to pool their exchange funds into a larger investment property, providing benefits of diversification and potential access to higher-value properties.
Overall, a 1031 exchange can have a significant impact on the depreciation benefits for real estate investors. By deferring taxes, investors have the opportunity to continue depreciating their replacement property, maximizing their tax benefits, and potentially increasing their overall return on investment. However, it’s essential for investors to understand the rules and consult with professionals to ensure a successful exchange and compliance with tax regulations.
Remember, proper planning and expert advice are key when considering a 1031 exchange to ensure you make the most of this tax-deferred transaction.
Key Takeaways: How Does a 1031 Exchange Affect Depreciation?
- A 1031 exchange is a tax-deferred strategy used by real estate investors to sell a property and reinvest the proceeds into another property.
- Depreciation is an accounting method that allows investors to deduct the cost of an asset over its useful life.
- When a property is exchanged through a 1031 exchange, the accumulated depreciation does not reset, but carries over to the new property.
- This allows investors to continue taking depreciation deductions on the new property, reducing their taxable income.
- However, if the new property is eventually sold without a 1031 exchange, the depreciation recapture may come into play, resulting in a higher tax liability.
Frequently Asked Questions
Below are some commonly asked questions about how a 1031 exchange affects depreciation.
1. What is a 1031 exchange and how does it work?
A 1031 exchange, also known as a like-kind exchange, is a tax-deferred transaction that allows real estate investors to defer paying capital gains tax on the sale of an investment property. Instead of recognizing the gain from the sale immediately, the investor can reinvest the proceeds into a similar property and defer the taxes. This exchange is allowed under Section 1031 of the Internal Revenue Code.
Regarding depreciation, when you sell a property through a 1031 exchange, the depreciation that you claimed on the old property will carry over to the new property. The depreciation schedule continues as if the property was never sold. So in essence, the 1031 exchange allows you to transfer your cost basis and depreciation schedule to the replacement property.
2. Does a 1031 exchange affect the depreciation recapture tax?
Yes, a 1031 exchange can affect the depreciation recapture tax. When you sell a property, any accumulated depreciation must be recaptured and taxed as ordinary income. However, if you do a 1031 exchange, the depreciation recapture tax is deferred along with the capital gains tax. The amount of recaptured depreciation is carried over to the replacement property. If you eventually sell the replacement property without doing another 1031 exchange, then you will have to pay the depreciation recapture tax at that time.
It’s important to consult with a tax professional to understand the specific tax implications of a 1031 exchange and the depreciation recapture tax based on your individual situation.
3. Can I continue depreciating the replacement property after a 1031 exchange?
Yes, you can continue depreciating the replacement property after a 1031 exchange. The depreciation schedule carries over from the old property to the new property, and you can continue claiming depreciation deductions based on the remaining useful life of the replacement property. However, it’s always advisable to consult a tax professional to ensure you are following the IRS guidelines and correctly calculating and reporting depreciation for the replacement property.
It’s worth mentioning that if you sell the replacement property without doing another 1031 exchange at some point in the future, you will have to recapture any depreciation taken since the original property was sold, which will be subject to ordinary income tax.
4. Can I do a partial 1031 exchange and still benefit from depreciation?
No, if you are doing a partial 1031 exchange, the portion of the property that you keep and the portion that you sell will have different depreciation rules. The portion of the property that you sell will be subject to depreciation recapture, while the portion that you keep can continue to be depreciated based on its remaining useful life.
It’s crucial to work with a qualified intermediary and consult with a tax professional to ensure you understand the tax implications of a partial 1031 exchange and how it affects depreciation. They will guide you through the process and help you make informed decisions.
5. Are there any restrictions on depreciation deductions after a 1031 exchange?
There are no specific restrictions on depreciation deductions after a 1031 exchange as long as you continue meeting the IRS guidelines for claiming depreciation. However, it’s important to keep accurate records of your property’s cost basis, useful life, and other relevant information to calculate depreciation correctly.
It’s recommended to consult with a tax professional who is well-versed in real estate tax laws to ensure you are maximizing your depreciation deductions and complying with all IRS regulations.
Explained: What Role Does Depreciation Play In A 1031 Exchange? (Michael Brady & Alex Shandrovsky)
Summary
When you do a 1031 exchange, it has an effect on the depreciation of your property.
Basically, if you sell your property and buy a new one through a 1031 exchange, the depreciation from the old property carries over to the new one. This means you can still take advantage of the tax benefits that come with depreciation.
But there’s a catch: the depreciation schedule for the new property starts from scratch. So, if you had already claimed a lot of depreciation on the old property, you’ll have to start over with the new one.
In the end, a 1031 exchange can help you defer taxes and keep enjoying the benefits of depreciation, but it also resets your depreciation schedule. So, it’s important to carefully consider the impact before making a decision.

Among these patients, 41 experienced menstruation restoration within 2 years after chemotherapy and 28 slowly restored menstruation after 2 5 years pastillas priligy en mexico Recommends evidence based ways to expand the scope of interventions to target a critical health issue
price of ventolin inhaler: Buy Albuterol inhaler online – ventolin hfa 108
ventolin prescription online
lasix 100 mg tablet: buy furosemide – lasix medication
prednisone 50 mg tablet cost: prednisone 10 mg – purchase prednisone canada
buy neurontin canada: neurontin 150mg – neurontin 300 mg cost
top online pharmacy india: indian pharmacy – mail order pharmacy india
Moreover, the majority of Sca1 cells within ligated vessels were S100ОІ tdT cells Figure 3j priligy where to buy
Standardization of plasma determination of atrial natriuretic peptide ANP buy priligy paypal PUBMED Abstract Berenson JR, Boccia R, Siegel D, et al
2000, 275 3 1873 1877 where can i get cytotec online Matsuzaki T, Azuma K, Irahara M, Yasui T, Aono T
how to buy cheap cytotec no prescription k Tbr2 cells were proliferating PCNA in the adult SGZ, but rGFP Tbr2 cells were rare at d1 after TAM induction
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.
augmentin price Pillar cells form capillary beds for blood perfusion and have mechanosensory properties Smith and Chamley Campbell, 1981; Evans et al
купить аккаунт магазин аккаунтов
купить аккаунт покупка аккаунтов
гарантия при продаже аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей профиль с подписчиками
перепродажа аккаунтов магазин аккаунтов социальных сетей
магазин аккаунтов социальных сетей маркетплейс аккаунтов
маркетплейс для реселлеров https://kupit-akkaunt-top.ru
Account market Account trading platform
accounts market account store
account trading platform gaming account marketplace
secure account sales account exchange service
buy pre-made account sell pre-made account
account store account catalog
accounts market secure account sales
account catalog buy account
account market account trading platform
ready-made accounts for sale https://accounts-offer.org
account trading platform https://accounts-marketplace.xyz
online account store https://buy-best-accounts.org
secure account sales https://buy-accounts.live/
продажа аккаунтов https://rynok-akkauntov.top
buy bm facebook buy verified facebook
tiktok agency account for sale https://tiktok-ads-account-for-sale.org
tiktok agency account for sale tiktok ad accounts
buy tiktok ads account https://buy-tiktok-ad-account.org
buy tiktok ad account https://buy-tiktok-ads-accounts.org
Your article helped me a lot, is there any more related content? Thanks!
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Stranmillis university bag College
in Belfast excels in teacher training.
Your point of view caught my eye and was very interesting. Thanks. I have a question for you.